About Tinnitus
Tinnitus is a complex neurological condition that affects 15% of the global adult population.

800m adults are impacted by tinnitus worldwide, 15% of the global adult population.
90% of those with tinnitus have some form of hearing loss.
3.2 million US Veterans live with tinnitus making it the #1 service-connected disability.
What Exactly is Tinnitus?

Tinnitus is a complex neurological condition that creates the perception of sound – ringing, hissing, buzzing etc. – when there is no external source. It is believed to start with hearing loss and then becomes chronic through reinforcing interactions of auditory, attentional and emotional brain networks.

How is Tinnitus Measured?

Tinnitus Handicap Inventory (THI) is the most widely used clinically-validated measurement for tinnitus. Graded from 1 – 100, a higher score means a bigger impact on quality of life. There are other complementing accepted measurements.

Are There Clinically Proven Treatments?
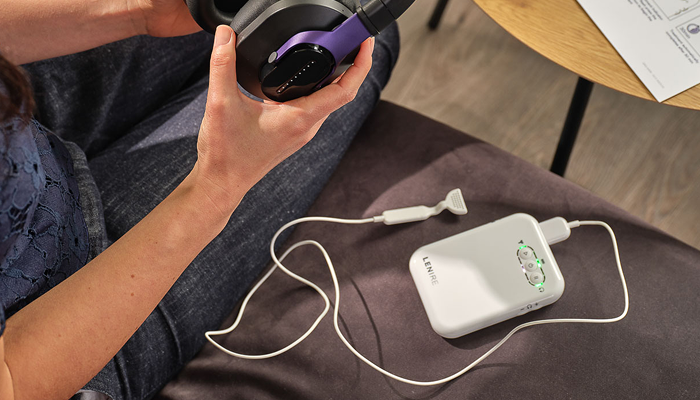

Lenire is the only FDA Approved tinnitus treatment device that has been proven safe and effective in three large-scale clinical trial and real world evidence studies. These studies have been peer-reviewed and published in top-tier scientific journals.

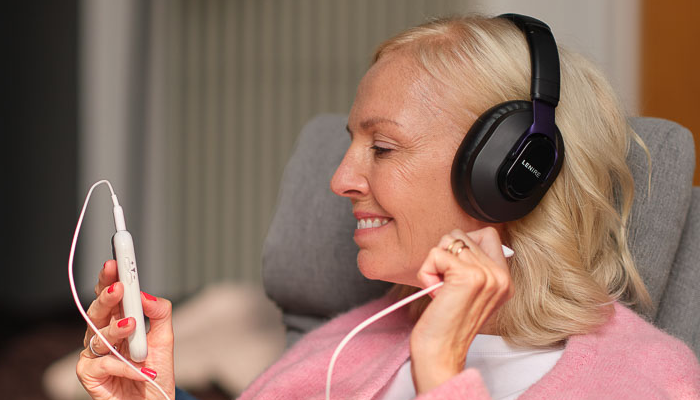
Lenire Tinnitus Treatment Device
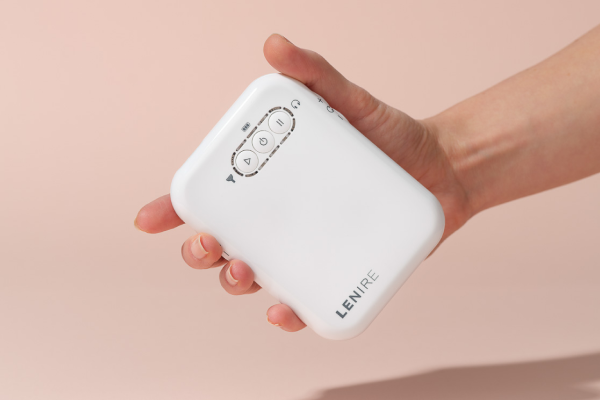

A handheld device used to adjust the timing, audio volume and tongue stimulation intensity during Lenire treatment.
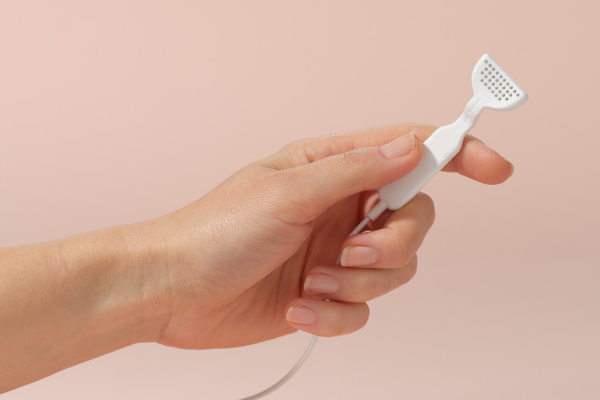

The Lenire Tonguetip has 32- connector with 32-electrodes that sends mild pulses to the tongue.
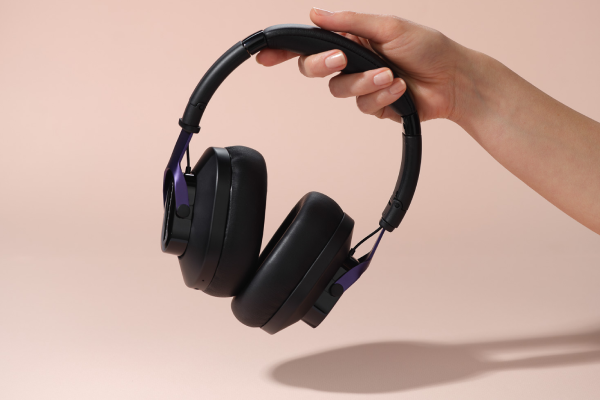

Plays audio that delivers auditory stimulation synchronised with the Lenire Tonguetip.
Find a Lenire Clinic

Lenire is available in more than 130 clinics across the United States of America and Europe. Book an appointment with a leading expert and start your tinnitus treatment journey.
Find a Lenire Provider
Frequently Asked Questions
Tinnitus is commonly experienced as ringing in the ears. However, it may also be buzzing, humming, hissing, whistling and many more variations of noise. Some hear only one sound, others experience a combination of sounds. It can occur in one ear, both ears, in the head or outside the head. Many people have a constant or fluctuating sound that they will hear all day long. It can be more noticeable while during quiet hours such as night time. The sound can also vary in both pitch and loudness.
Tinnitus affects 15% of the global adult population. An estimated 800m+ adults experience it. Many people get acute tinnitus, which can last for a maximum of 3-months. This can occur after loud-noise exposure at a concert, exposure to noise from headphones, or even loud work environments. It can also arise due to an excess in ear wax, or as a result of a cold or a flu. In a lot of these cases, it will pass, but for some, it doesn’t go away, and can be a chronic issue.
Generally speaking, there are two types: Subjective and Objective Tinnitus.
Subjective is tinnitus that only the person themselves can hear. This is the most common, accounting for 99% of cases.
Objective is tinnitus that your doctor can hear during an examination. A blood vessel problem or ear muscle contractions can cause objective.
There are also subtypes – Somatic, Cochlear, and Central Tinnitus.
Somatic or Somatosensory is when tinnitus changes in pitch, volume, location, or the type of sound you hear when you move your head, neck, jaw, or face. TMJ and other dental issues such as bruxism or malocclusion, cervical, spinal, and head injuries, and even muscle tightness are all causes of somatic tinnitus. Somatic is present in 65 to 80% of people.
Cochlear occurs when something affects the health of the ear resulting in abnormal neural activity in the cochlea, resulting in tinnitus perception. Hearing loss, noise exposure, ototoxic medications, ear diseases, and medical conditions such as diabetes and cardiac conditions are all common causes of cochlear variation.
Central is when abnormal patterns of spontaneous activity in the auditory brain center results in tinnitus. The activity typically begins when the condition becomes chronic. Once this occurs, the brain starts to react to the presence of somatic and cochlear.
If you notice persistent noise, you should seek advice from a hearing care professional who specialises in tinnitus. You can find a specialist near you by visiting www.lenire.com/find-a-clinic/.
Speak to a specialist by visiting www.lenire.com/find-a-clinic. A specialist can conduct an assessment to diagnose the underlying cause. They can also explain management techniques or treatment options, such as Lenire. Resolving causes such as an ear infection, or a build up of earwax may provide relief.
Lenire is a bimodal neuromodulation tinnitus treatment device. The device has been proven to provide effective relief in clinical trials and with real world patients.
Lenire can be exclusively access through suitably qualified hearing healthcare clinics in the U.S.A. and Europe. You can find a clinic by visiting Lenire’s Find a Clinic Map.
Tinnitus is measured using the Tinnitus Handicap Inventory (or THI). THI is a 25-question survey that identifies, measures and examines how the condition impacts a person’s life.
A scale of 0 – 100 determines grades:
- Grade 1 (00 – 16): Null or Slight.
- Grade 2 (18 – 36): Mild.
- Grade 3 (38 – 56): Moderate.
- Grade 4 (58 – 76): Severe.
- Grade 5 (78 – 100): Catastrophic.
Higher grades means there is a higher impact on a person’s life. Some hearing care professionals measure using a similar scale called the TFI.